Adenium Flower Plant: Care, Growth, and Blooming Guide
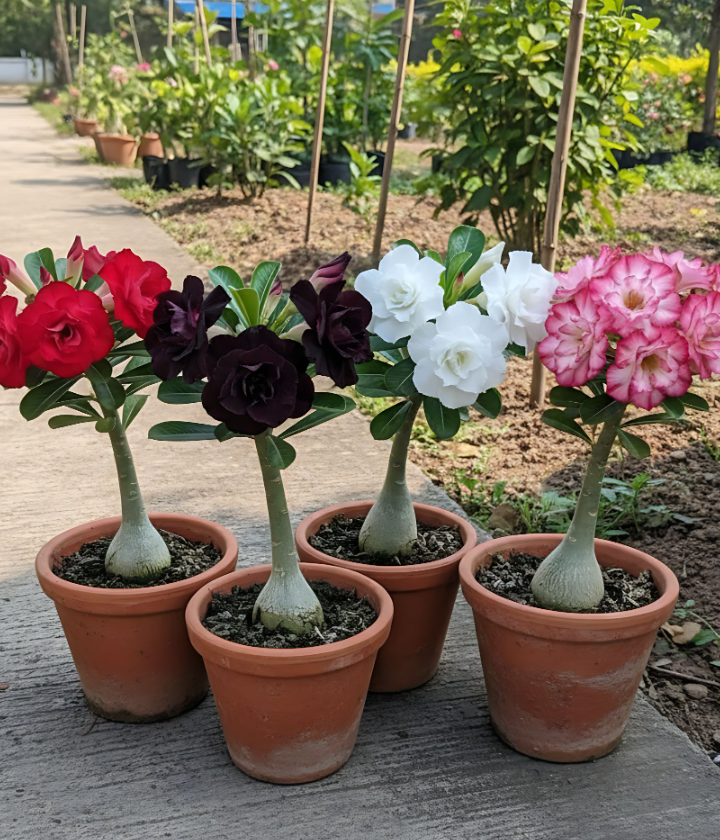
The Adenium flower plant, commonly known as the Desert Rose, is a unique and captivating flowering plant cherished for its striking blooms and unusual, sculptural trunk. Native to arid regions of Africa and the Arabian Peninsula, Adenium thrives in sunny, warm environments and can be grown successfully indoors or outdoors in the right conditions.
Its vibrant flowers, ranging from deep red to pink and white, combined with its swollen caudex and glossy leaves, make it a favorite among bonsai enthusiasts and ornamental plant lovers alike. Understanding how to care for Adenium properly ensures it remains healthy, resilient, and blooms repeatedly year after year.
Understanding the Adenium Plant
Adenium is a succulent, which means it stores water in its thickened stem and roots, enabling it to survive in drought-prone environments. Its natural habitat exposes it to intense sunlight, high temperatures, and well-drained soils. Knowing these preferences helps replicate the ideal conditions at home.
Key characteristics include:
- Thickened caudex (swollen stem base) for water storage
- Glossy green leaves, often clustered at branch tips
- Striking trumpet-shaped flowers in multiple shades
- Deciduous behavior: shedding leaves during dormant periods
Choosing the Right Location
Light is one of the most crucial factors for Adenium flowering. The plant requires:
- Full sun for at least 6 hours per day
- Warm temperatures, ideally above 65°F (18°C)
- Protection from frost and extreme cold
Indoors, place your Adenium near the sunniest window. Outdoors, a balcony, terrace, or garden area with direct sunlight works best.
Soil Requirements
Adenium requires extremely well-draining soil to prevent root rot. The best soil mix combines:
- Cactus or succulent soil as the base
- Perlite or coarse sand for drainage
- Optional: small amounts of organic matter for nutrients
Avoid dense garden soil or clay, which can retain water and harm the plant.
Watering Adenium Properly
Adenium’s water needs change throughout the year. Overwatering is the most common reason for plant loss.
Active Growth Period (Spring & Summer)
- Water deeply when the top 1–2 inches of soil are dry
- Allow water to drain fully from the pot
- Do not let the plant sit in standing water
Dormant Period (Fall & Winter)
- Water very sparingly
- Allow the soil to dry completely between watering
- Focus on keeping the plant cool and dry
The key is patience and observation: the plant should look plump and healthy, not wilted or mushy.
Fertilizing for Flowers
Adenium blooms best when given light, consistent fertilization during the growth period.
- Use a balanced, water-soluble fertilizer (10-10-10 or cactus fertilizer)
- Feed every 4–6 weeks during spring and summer
- Avoid fertilizing during dormancy
- Optional: a small dose of Epsom salt occasionally to encourage vibrant flowers
Pruning and Shaping
Pruning helps Adenium maintain a compact shape, encourages branching, and increases flower production.
- Prune in late winter or early spring before growth begins
- Cut back leggy or weak branches
- Remove any dead or diseased wood
- Bonsai enthusiasts may also trim roots to encourage a thick caudex
Pruning should be gentle; avoid removing more than 30% of the plant at once.
Encouraging Year-Round Blooms
Adenium blooms when it experiences stress-free growth in warm, sunny conditions with proper watering. Some tips include:
- Provide full sunlight daily
- Feed lightly with flower-promoting fertilizer
- Keep soil slightly on the dry side between waterings
- Prune older branches to stimulate new growth
- Maintain good airflow to prevent pests and disease
Patience is essential. Flowers usually appear during warmer months, but healthy care may encourage multiple blooming periods per year.
Common Pests and Diseases
Adenium is relatively hardy but can face issues:
- Aphids: remove with water spray or insecticidal soap
- Spider mites: increase humidity and clean leaves regularly
- Root rot: caused by overwatering; ensure excellent drainage
- Fungal leaf spots: avoid wetting leaves and provide airflow
Regular inspection and proper cultural care usually prevent most problems.