9 Things You Should Never Plug Into a Power Strip
Power strips are everywhere.
Under desks. Behind entertainment centers. In dorm rooms. In home offices.
They make it easy to charge phones, power laptops, and run lamps without crawling behind furniture.
But here’s what many people don’t realize:
Not everything belongs on a power strip.
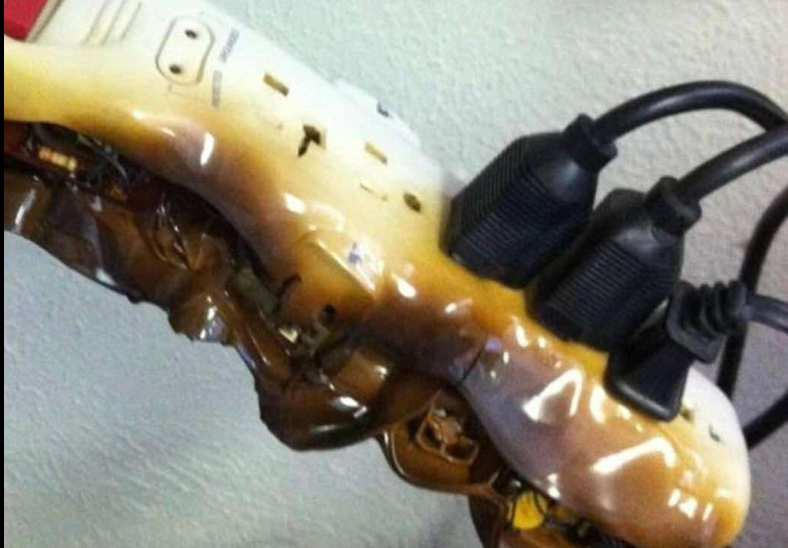
Power strips are designed for low-power electronics — not high-wattage appliances. Overloading them can lead to overheating, melting insulation, damaged wiring, and even electrical fires.
According to the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission, thousands of residential fires each year are linked to misuse of power strips and surge protectors.
Real convenience isn’t about plugging everything in.
It’s about knowing what shouldn’t go in.
⚠️ Why Power Strips Have Limits
Power strips are not independent power sources.
They are simply extensions of your wall outlet — and your wall outlet is limited by the circuit it’s connected to.
Key Facts
- ✅ Most household power strips are rated for 15 amps (about 1,800 watts).
- ❗ Multiple high-draw appliances can easily exceed this limit.
- 🚫 Daisychaining (plugging one strip into another) dramatically increases fire risk.
- 🔥 Overloaded strips can overheat → melt insulation → ignite nearby materials.
Rule of thumb: Use power strips only for low-power electronics. Never use them as a permanent substitute for adequate wall outlets.
Now, let’s look at what should never be plugged into one.
1. Space Heaters
Space heaters are among the most common causes of overload.
- Typical wattage: 1,000–1,500 watts
- Near the maximum rating of most power strips
- Generate intense heat continuously
Plugging a space heater into a strip increases the risk of overheating and fire.
Safer choice: Plug directly into a dedicated wall outlet.
2. Refrigerators & Freezers
These appliances cycle on and off, drawing large bursts of power when the compressor starts.
- High startup current (surge draw)
- Risk of strip failure during power spikes
- Potential food spoilage if tripped
They require a stable, grounded outlet.
3. Microwaves
Microwaves draw heavy power — often between 1,000 and 1,500 watts.
That’s nearly the full capacity of many power strips by itself.
Adding anything else to the strip at the same time? Dangerous overload.
Always plug directly into a wall outlet.
4. Coffee Makers
Heating elements demand high wattage, especially during brewing.
- Rapid heating cycles
- High sustained load
- Often left unattended
These factors increase fire risk when used with a power strip.
5. Toasters & Toaster Ovens
Small but powerful.
Toasters can draw over 1,200 watts.
Toaster ovens can draw even more.
They should always be plugged directly into a wall outlet due to:
- High heat output
- Crumb accumulation risk
- Electrical load demand