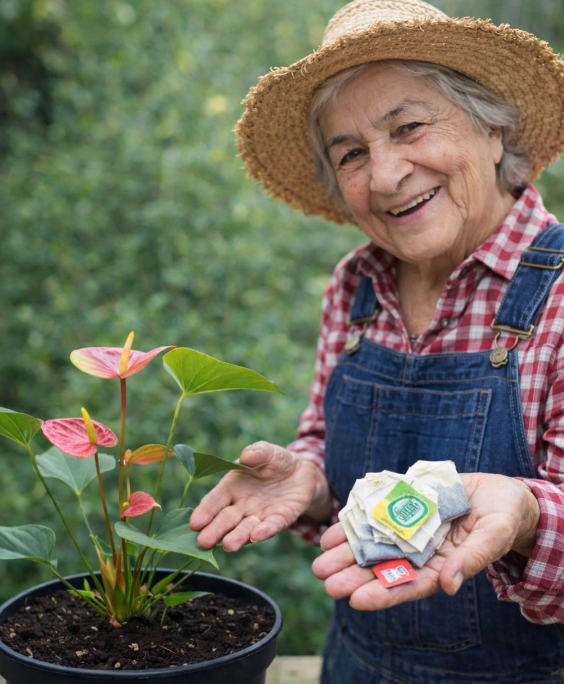
Don’t Throw Away Used Tea Bags — Turn Them Into Natural Fertilizer for Healthier, Greener Plants
Most people brew their morning tea, squeeze the bag, and toss it straight into the trash.
But what if that small, soggy tea bag still holds value?
Hidden inside those used leaves are nutrients, organic matter, and soil-enhancing compounds that many gardeners are quietly using to grow stronger, greener plants — without spending extra money on commercial fertilizers.
This simple, old-fashioned gardening trick is gaining attention again. And for good reason.
If you’re looking for a sustainable, low-cost way to enrich your soil and support plant health, used tea bags might be one of the easiest upgrades you can make.
Let’s explore why it works, how to use it safely, what it costs (almost nothing), and which plants benefit the most.
🌿 Why Used Tea Bags Are Good for Plants
Tea leaves contain small amounts of nutrients and organic compounds that plants and soil microbes can benefit from when used properly.
According to soil health researcher Dr. Leila Nour, “Organic matter is one of the most valuable additions to garden soil. Even small contributions, like composted tea leaves, can improve structure and microbial balance over time.”
Key Components Found in Tea Leaves
- Nitrogen – Supports leafy green growth
- Tannins – May slightly influence soil acidity
- Organic matter – Feeds beneficial microbes
- Trace minerals – Present in small quantities
When tea leaves decompose in soil, they break down slowly, enriching the surrounding area naturally.
However, it’s important to understand that tea bags are a soil supplement, not a complete fertilizer replacement.
🌱 How Tea Bags Improve Soil Quality Over Time
Healthy soil isn’t just about nutrients — it’s about structure.
Horticulture consultant Professor Mark Benson explains, “Soil that contains diverse organic materials retains moisture better and supports root development more effectively than compacted, lifeless soil.”
Used tea leaves can help:
- Improve moisture retention
- Encourage earthworm activity (outdoor gardens)
- Enhance soil texture
- Support beneficial microbial populations
In container gardening, small organic additions can make potting mix more resilient over time.
📊 Nutritional & Functional Value of Used Tea Leaves
| Component | Approximate Contribution | Application Amount | Functional Benefit | Practical Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen (Trace) | Low concentration | 1 used tea bag per small plant | Supports leafy growth | Gentle nutrient boost |
| Organic Matter | Moderate | 1–2 bags per 8–10 inch pot | Improves soil structure | Enhances moisture retention |
| Tannins | Variable | Occasional use | May influence soil acidity | Helpful for some acid-loving plants |
🌸 Benefits of Using Tea Bags as Fertilizer
1️⃣ Improves Soil Quality
As tea leaves decompose, they enrich the soil with organic material.
2️⃣ Supports Leaf Growth
Nitrogen contributes to greener foliage when used moderately.
3️⃣ Eco-Friendly Gardening
Reusing tea reduces waste and promotes sustainable habits.
4️⃣ Saves Money
Instead of buying soil amendments frequently, you recycle what you already use.
💧 How to Use Tea Bags Safely in Your Garden
Step 1: Cool Completely
Let the tea bag cool after brewing.
Step 2: Check the Material
Ensure the tea bag is biodegradable. Some brands contain plastic fibers that don’t break down.
Step 3: Bury Near Roots
Place directly into soil a few inches below the surface.
Step 4: Alternative Method
Open the bag and sprinkle leaves directly into soil or compost.
Step 5: Water Normally
Continue regular watering routine.
Plant care educator Sarah Coleman advises, “Moderation prevents mold. Avoid placing tea bags on top of soil where they stay wet and exposed.”
🆚 Tea Bags vs Commercial Fertilizer
🌿 Tea Bags
- Free and sustainable
- Slow nutrient release
- Improves soil structure
- Not nutrient-dense
🧴 Commercial Fertilizer
- Balanced nutrient ratios
- Faster visible growth
- More predictable results
- Higher cost
Best strategy? Use tea bags as a supplement, not a replacement for balanced feeding.